Research
I am broadly interested in machine learning, control, and optimization. My goal is to make AI systems work safely and reliably in the real world.
Representation Learning for Goal-Conditioned Planning
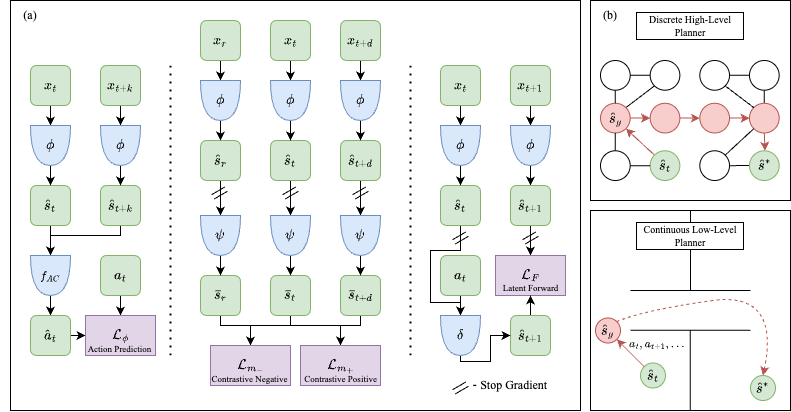 We discover a latent state representation conforming with the geometry of the environment from the high-dimensional observation data of the controllable agent. A multi-step inverse dynamics is learned to remove distracting information and a temporal constrastive learning method is applied to capture reachability of the environment in the latent space with respect to the Euclidean norm. Built on the learned latent representation and latent dynamics, we construct a computationally efficient hierarchical motion planner with boosted sampling efficiency.
We discover a latent state representation conforming with the geometry of the environment from the high-dimensional observation data of the controllable agent. A multi-step inverse dynamics is learned to remove distracting information and a temporal constrastive learning method is applied to capture reachability of the environment in the latent space with respect to the Euclidean norm. Built on the learned latent representation and latent dynamics, we construct a computationally efficient hierarchical motion planner with boosted sampling efficiency.
Scalable Neural Network Verification
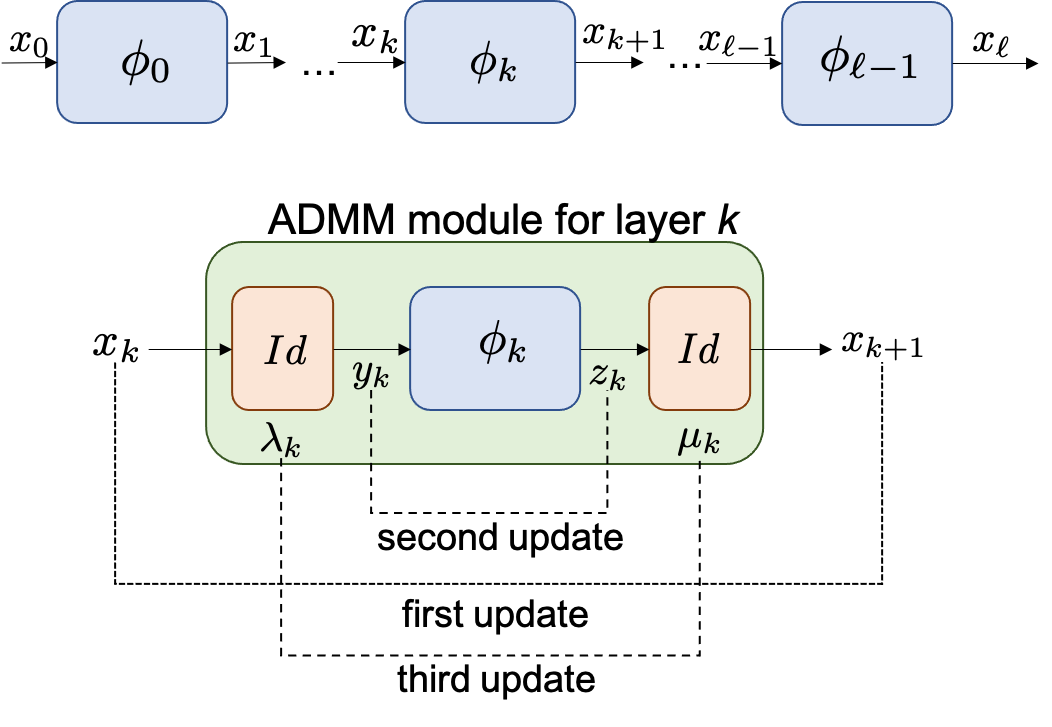 Neural network verification considers the problem of certifying if the output of a NN satisfies certain properties for a given input set. This is a fundamental problem in certifying the robustness of NNs and the safety of NN-controlled systems.
Neural network verification considers the problem of certifying if the output of a NN satisfies certain properties for a given input set. This is a fundamental problem in certifying the robustness of NNs and the safety of NN-controlled systems.
In J2, we use Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM) to derive a NN verification method, DeepSplit, that is scalable, modular, amenable to GPU acceleration and enjoys fast theoretical convergence guarantees.
Verification-Aided Learning of Neural Ceritifcates
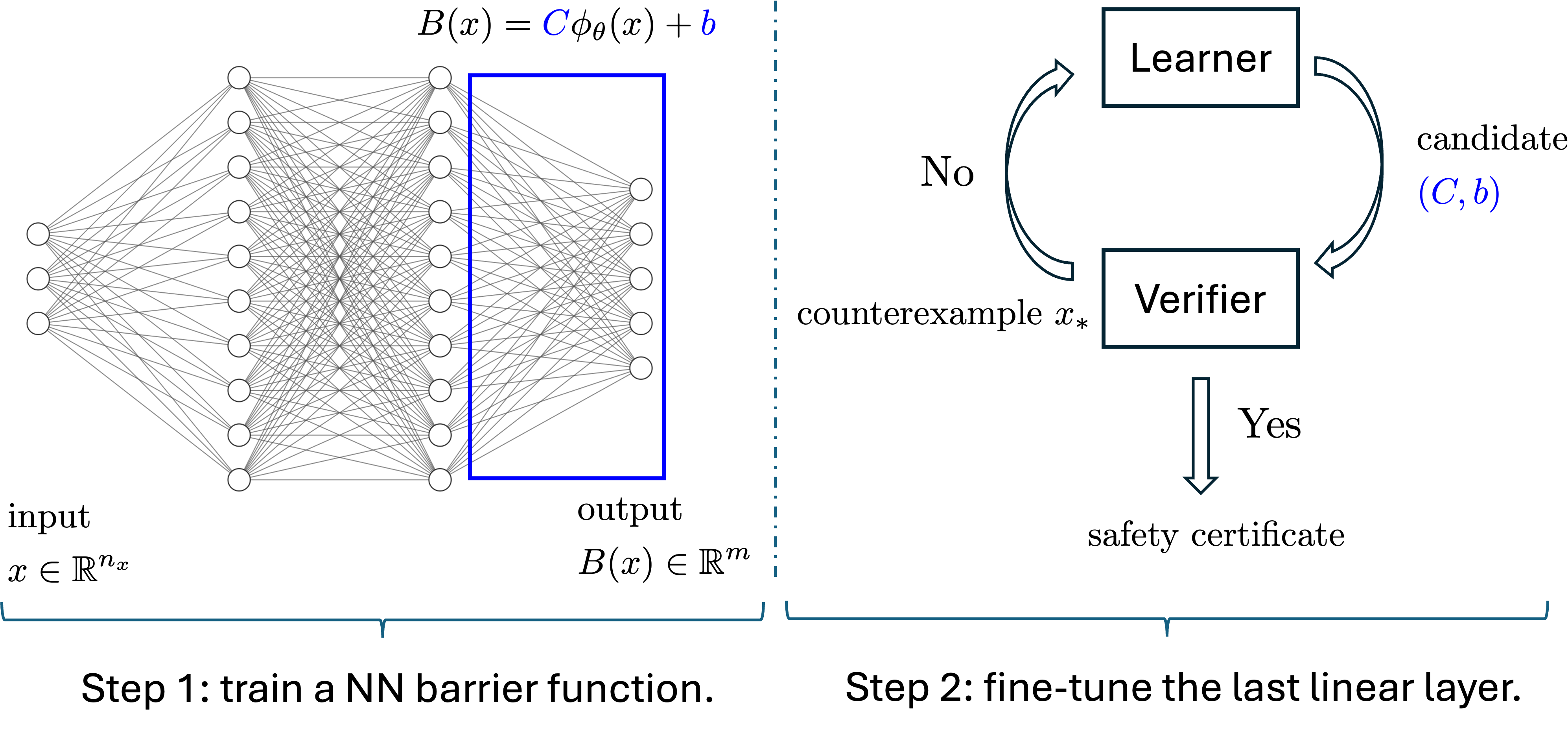 It is easy to approximately learn a neural network certificate for an AI system, but to get a formal one is difficult. Using verification tools to find counterexamples for the learned neural certificates, we can iteratively refine the learned neural certificates toward a formal one. In C11, we reveal the continual learning nature of such a procedure and propose a fine-tuning approach for the solution refinement. The fine-tuning method is based on the cutting-plane method from convex optimziation, and a strong convergence guarantee of the iterative refinement procedure is provided. Our method can significantly boost the success rate of learning a formal neural certificate.
It is easy to approximately learn a neural network certificate for an AI system, but to get a formal one is difficult. Using verification tools to find counterexamples for the learned neural certificates, we can iteratively refine the learned neural certificates toward a formal one. In C11, we reveal the continual learning nature of such a procedure and propose a fine-tuning approach for the solution refinement. The fine-tuning method is based on the cutting-plane method from convex optimziation, and a strong convergence guarantee of the iterative refinement procedure is provided. Our method can significantly boost the success rate of learning a formal neural certificate.
Safety and stability analysis of learning-enabled systems
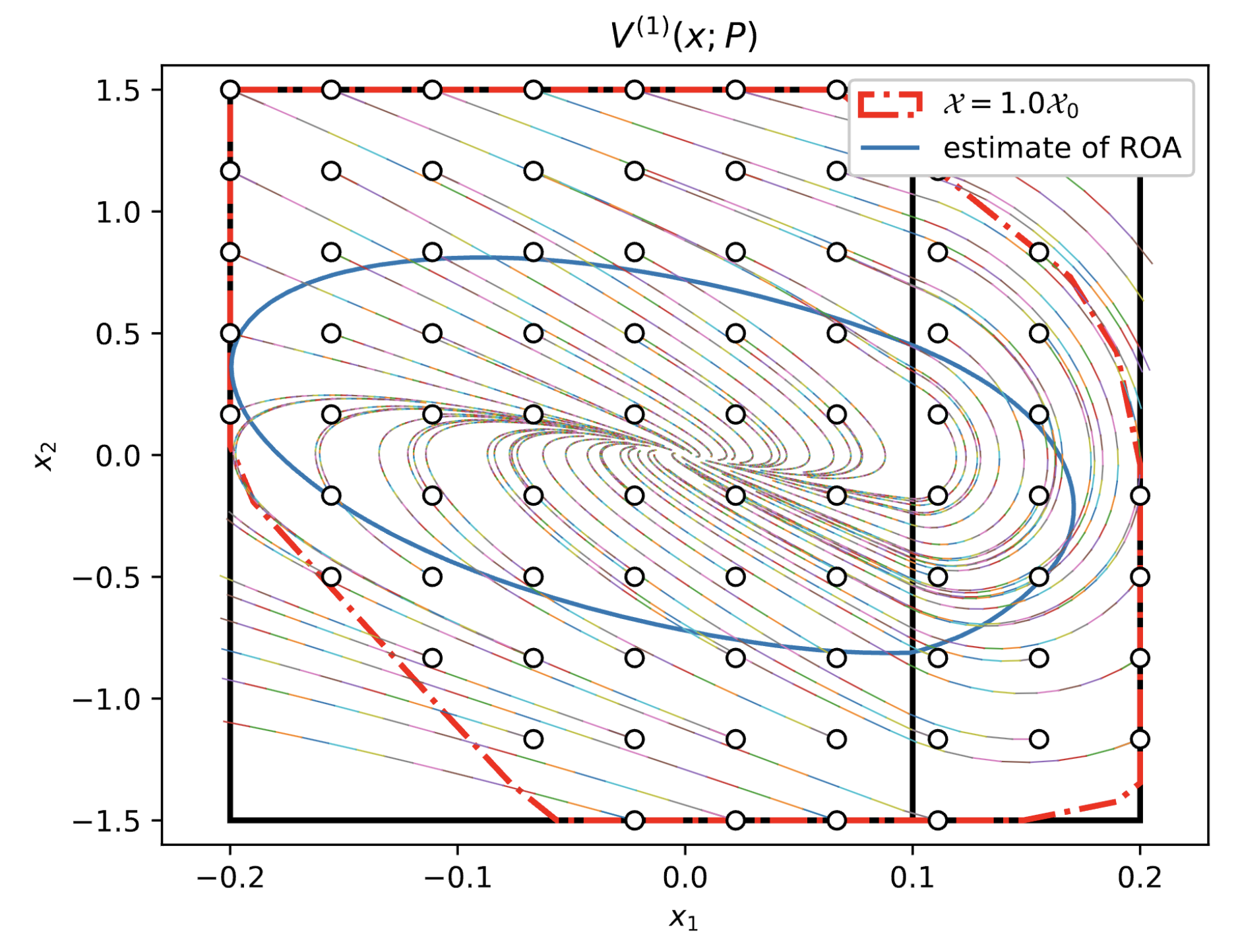
Learning for control works great, but the gap between research in labs and deployment in the real world is hard to close. The coupling of learning modules and dynamical systems significantly complicates the analysis of the system’s behavior. How can we make this leap to achieve assured autonomy?
For learning-enabled systems, we analyze their reachability in C9 and stability in C6, C7. In reachability analysis, we rigorously characterize the conservatism-complexity trade-off when using NN verification tools. In stability analysis, we draw tools from convex optimization to learn a Lyapunov function with convergence guarantees.
Boosting tightness of robust model predictive control
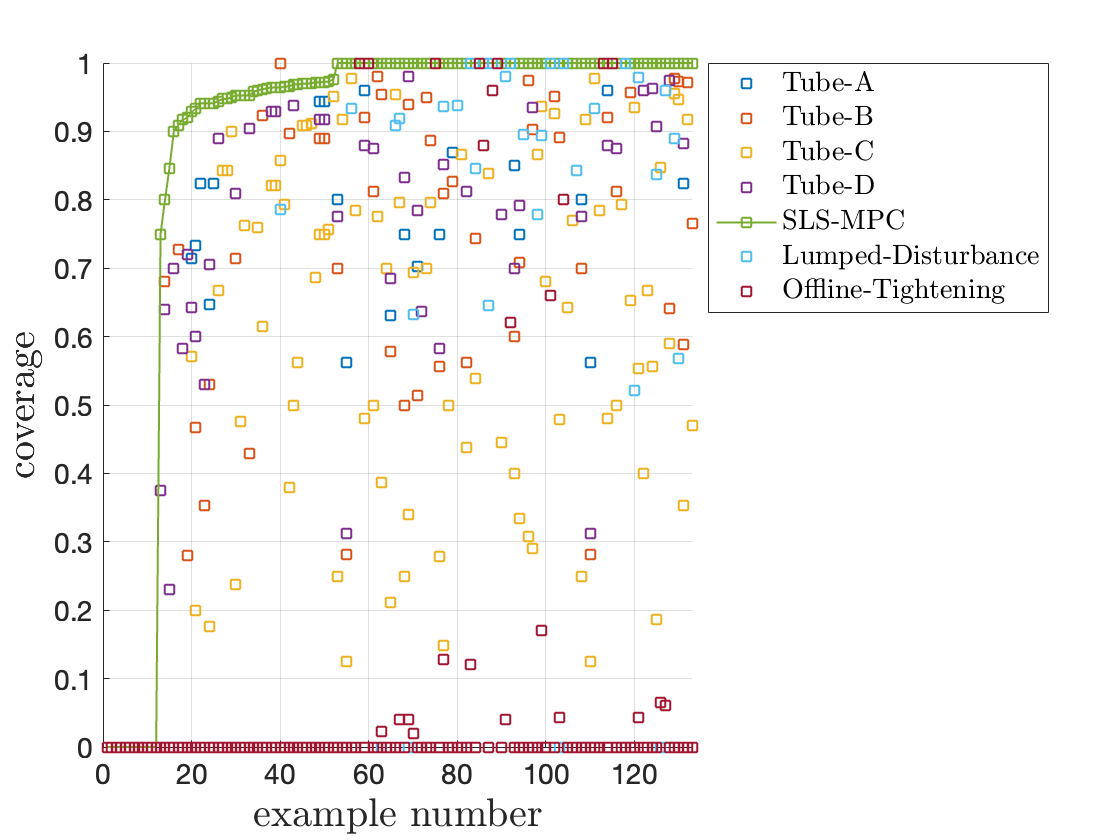
Model predictive control (MPC) is widely applied in robotic and cyber-physical systems. Robust MPC takes model uncertainties and disturbances explicitly into account when designing feedback policies. It gives rise to a challenging robust optimization problem where the effects of uncertainty and feedback policy are intertwined.
In J4, we propose a novel robust MPC method, SLS MPC, using System Level Synthesis and search for robust feedback controllers in the space of closed-loop system responses. This parameterization reveals additional structured properties of the robust control problem and leads to a significant tightness improvement of robust MPC.
Online safety filter design for learning-enabled systems
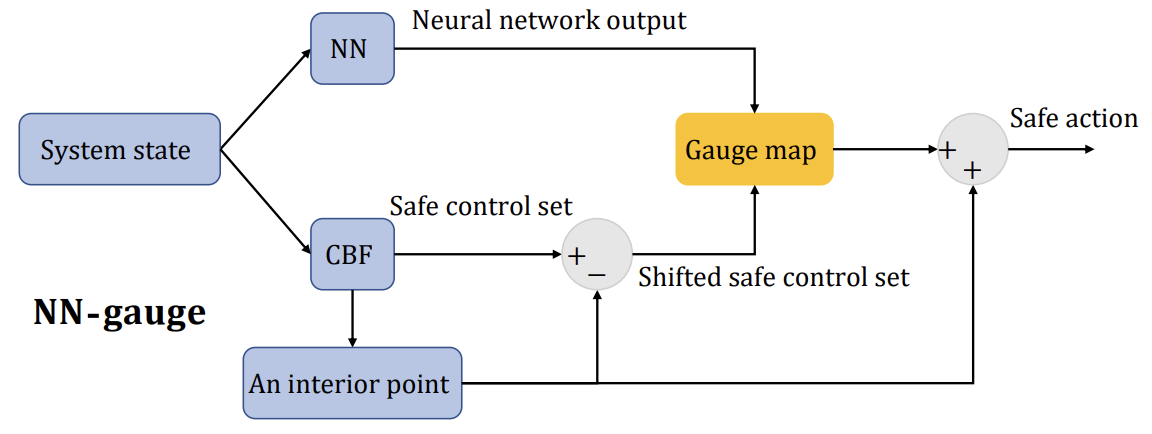
A safety filter monitors the output of a reference policy online and corrects any unsafe actions to guarantee the safety of the system. It enjoys modularity and theoretical soundness, making it a popular and promising tool for safe learning-based control. However, it remains a challenge to design a safety filter for complex dynamics.
In C10, we design a convex optimization-based predictive safety filter for NN dynamical systems by fusing NN verification with robust MPC. In J3, we propose a safe-by-construction NN policy using control barrier functions.
